On this page
Launch Templates and Tenancy
A launch template specifies instance configuration (AMI ID, instance type, key pair, security groups, etc.).
Default tenancy: shared .
Tenancy behavior:
Launch Template: shared, VPC: dedicated → dedicated tenancy
Launch Template: dedicated, VPC: default → dedicated tenancy
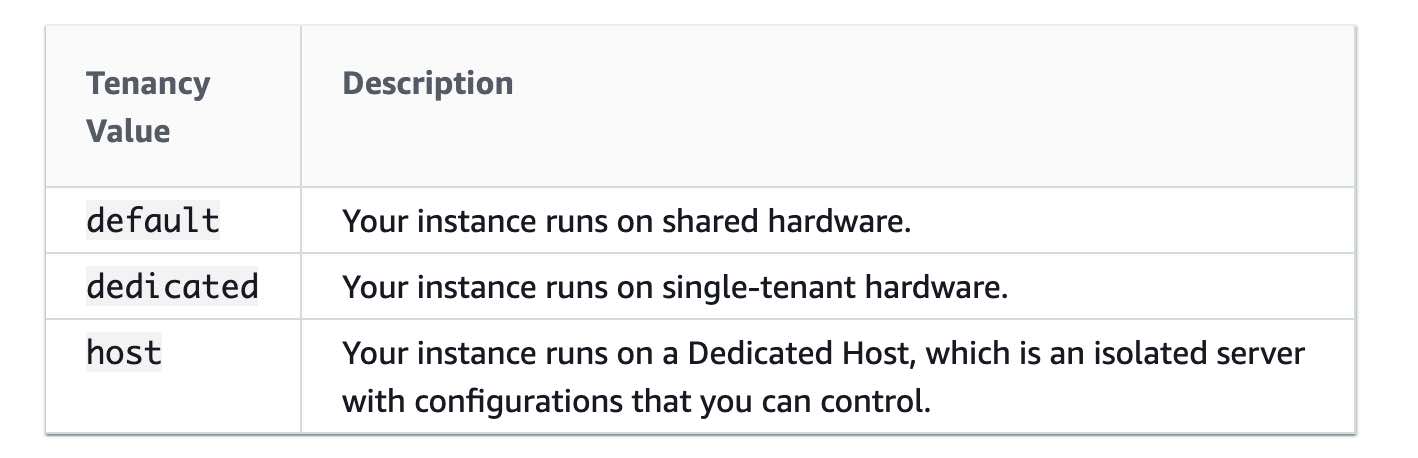
EC2 Tenancy Options
By default, Amazon EC2 instances run on shared tenancy .
Dedicated Instances :
Run on hardware dedicated to one customer.
Isolated across AWS accounts but can share hardware across instances within same account.
Dedicated Hosts :
Full control over instance placement.
Visibility into physical server.
EC2 Spot Instances
Spot Instance = unused EC2 at reduced price.Pricing is determined by long-term demand/supply in each AZ.
Spot Instance request types:
Persistent requests reopen after interruption.
Spot Fleets maintain target capacity by launching replacements.
Canceling requests:
May or may not terminate instance depending on config.
EC2 Recovery
Recover impaired EC2 instance using CloudWatch alarms .Recovery applies to hardware failure or AWS-repairable issues.
Preserves:
Instance ID
Private & Elastic IPs
Metadata
If instance is in a placement group, recovery remains within group.
Note: Data in memory is lost.
🧠 Amazon EBS Volume Types — Memorize Like a Pro
✅ Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1) — Best for High IOPS Needs
Backed by : SSD (Solid-State Drives)Use Case : Mission-critical, I/O-intensive workloads (e.g., production-grade databases )IOPS Performance :
Up to 50 IOPS/GB
Max 64,000 IOPS per volume
Throughput : Up to 1,000 MB/s per volumeWhy Choose : Meets use-case needing 25,000 IOPS
❌ Incorrect Choices (Not suitable for high IOPS needs)
🟡 General Purpose SSD (gp2) — Balanced for General Use
Backed by : SSDUse Case : Dev/Test, Boot volumes, Web serversMax IOPS : 16,000 IOPS (not sufficient for 25k+)Throughput : Moderate🧠 Good all-rounder, but not built for intense workloads
🔵 Cold HDD (sc1) — For Archival Storage
Backed by : HDD (Hard Disk Drive)Use Case : Infrequently accessed, cold datasetsMax IOPS : 250 IOPS Throughput : Low🧠 Think: Cheap, cold storage for backups
🟣 Throughput Optimized HDD (st1) — For Big, Streaming Data
Backed by : HDDUse Case : Throughput-intensive workloads (e.g., MapReduce, Kafka, ETL, log processing)Max IOPS : 500 IOPS Throughput : High🧠 Great for throughput, bad for high IOPS
�🔑 Summary Table
Volume Type Backed By Max IOPS Best For io1 SSD 64,000 High IOPS DBs gp2 SSD 16,000 Dev/Test st1 HDD 500 Big data streaming sc1 HDD 250 Archival
FSx for Lustre
Use FSx for Lustre with Scratch File System for:
Temporary storage
Short-term data processing
No replication, non-persistent if a file server fails.
Up to 6× burst throughput of baseline 200 MBps/TiB.
Amazon Redshift
Amazon Redshift is a fully managed petabyte-scale data warehouse in the cloud.Can be a target for data migration from other databases.
Route 53: Alias vs CNAME
Amazon Route 53 :
No charge for alias queries , but charges for CNAME.Alias → AWS resources only (S3, CloudFront, same hosted zone).
CNAME → Any DNS record.
At zone apex (covid19survey.com):
Cannot create CNAME
Can create alias (e.g., point to www.covid19survey.com)
Internet Gateway
Internet Gateway :
Acts as route target for internet-bound traffic.
Performs network address translation (NAT) for public IPv4 instances.
Amazon SQS Polling
Amazon SQS supports:
Short polling : immediate response, may be empty.Long polling : waits for messages up to a timeout.
Long polling makes it inexpensive to retrieve messages, reducing cost and empty receives.
Amazon SQS FIFO Throughput
By default, FIFO queues support up to 3,000 messages/sec with batching.
Without batching: up to 300 messages/sec (send, receive, or delete operations).
Batching enables meeting higher throughput requirements (up to 3,000 messages/sec).
StackSet = CloudFormation + multi-account + multi-region.Uses one template from admin account.
Provisions into target accounts/org units across regions.
Elastic Load Balancer: Connection Draining
Elastic Load Balancing :
Uses connection draining for:
De-registering or unhealthy instances.
Preserves existing connections until timeout (1–3600s, default: 300s).
After timeout, force-closes remaining connections.
DynamoDB Global Tables
Active-active configuration in DynamoDB global tables :
No failover – data is written regionally and replicated.
More expensive than Aurora Global Database.
VPC Sharing
VPC sharing via Resource Access Manager (RAM) :
Allows multiple accounts to deploy resources in a shared VPC.
Owner shares subnets (not VPC itself) with org participants.
Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA)
Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA) :
Enhances HPC and ML inter-instance communication.
Adds OS-bypass interface to ENA features.
User-space apps can access transport directly for performance.
Elastic Cache
Amazon ElastiCache can be used to significantly improve latency and throughput for many read-heavy application workloads
(such as social networking, gaming, media sharing, leaderboard, and Q&A portals) or compute-intensive workloads (such as a recommendation engine) by allowing you to store the objects that are often read in the cache.